Back pain in kids is relatively uncommon, and most cases are temporary and not serious. However, there are various potential causes of back pain in children, and it’s essential to pay attention to certain factors to determine when it may be a cause for concern. Here are some common causes of back pain in kids:
1. Muscle Strain or Sprain
- Heavy backpacks: Carrying heavy backpacks or wearing them improperly can strain the muscles and cause back pain.
- Overexertion: Participation in sports or activities that involve repetitive or strenuous movements may lead to muscle strain
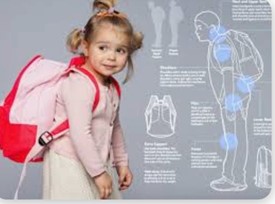
2. Poor Posture
- Spending extended periods in positions that strain the back, such as slouching or sitting for long periods, can contribute to back pain

3. Scoliosis
- Scoliosis is an abnormal curvature of the spine. It can cause back pain, although many children with scoliosis do not experience pain.
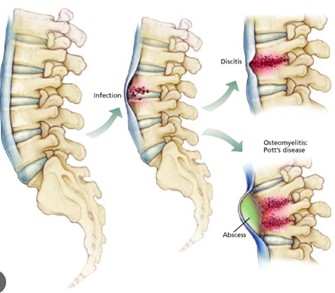
4. Infection
- Infections of the spine or surrounding tissues can cause back pain. This is less common but should be considered, especially if the pain is persistent or associated with other symptoms like fever.
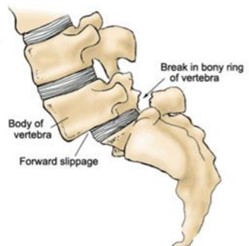
5. Structural Issues
- Structural problems in the spine, such as spondylolysis or spondylolisthesis, can cause back pain in children.
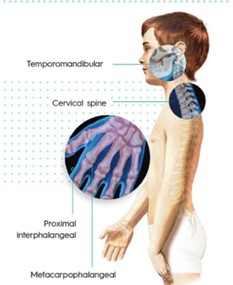
6. Inflammatory Conditions
- Conditions like juvenile idiopathic arthritis can affect the joints and cause back pain.
7. Psychosocial Factors
- Emotional stress, anxiety, or other psychosocial factors can sometimes manifest as physical symptoms, including back pain.
When to Worry
While most cases of back pain in children are not serious, there are certain signs and symptoms that may indicate a more concerning underlying issue. You should seek medical attention if your child experiences
Severe or Persistent Pain
- If the pain is severe, persists for an extended period, or is getting worse, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional
Fever
- Back pain accompanied by fever may suggest an infection and should be evaluated promptly
Trauma or Injury
- If the back pain is the result of a recent injury or trauma, especially if there’s a visible deformity or if the child is unable to move, seek medical attention immediately.
Neurological Symptoms
- Symptoms such as numbness, tingling, weakness, or changes in bowel or bladder function may indicate a more serious issue and require immediate medical attention.
Pain at Night
- Back pain that wakes a child from sleep or is more severe at night may be a cause for concern.
Always consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your child’s back pain. They can help determine the cause and recommend appropriate treatment or further evaluation if necessary.
Preventive tips for back pain in children
Preventing back pain in children involves promoting good posture, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and addressing factors that may contribute to musculoskeletal strain. Here are some preventive tips
Proper Backpack Use
- Ensure that your child’s backpack is the right size for their body and that they wear it correctly. The backpack should be worn over both shoulders with the straps adjusted to keep the load close to the body
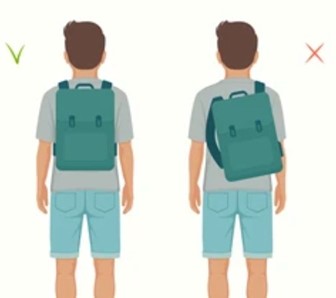
Limit Heavy Loads
- Encourage your child to carry only what is necessary in their backpack. Help them organize their belongings to distribute weight evenly
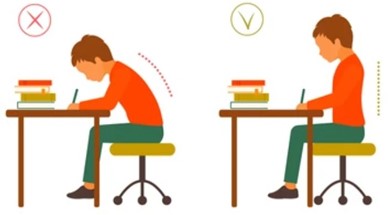
Encourage Good Posture
- Teach your child the importance of good posture, whether sitting, standing, or walking. Remind them to keep their shoulders back and their spine straight.
Regular Exercise
- Encourage your child to engage in regular physical activity. Strengthening exercises for the core and back muscles can help support the spine and reduce the risk of injury.

Limit Screen Time
- Discourage excessive screen time, especially activities that involve poor posture, such as prolonged use of smartphones or tablets. Encourage breaks and proper ergonomics when using electronic devices.

Ergonomic Workspaces
- Ensure that your child’s study or computer desk is ergonomically designed. The chair should provide good support, and the desk height should allow for proper posture

Healthy Lifestyle
- Encourage a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, proper hydration, and sufficient sleep. A healthy body is better equipped to handle physical stress.

Regular Health Check-ups
- Schedule regular check- ups with a healthcare provider. They can monitor your child’s growth and development and address any concerns about posture or musculoskeletal health.

Limit Sedentary Activities
- Discourage prolonged periods of sitting or inactivity. Encourage breaks, stretching, and movement throughout the day.
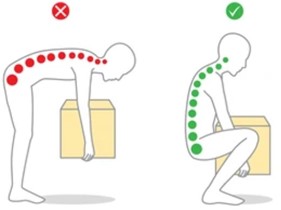
Educate About Lifting Techniques
- Teach your child proper lifting techniques. When picking up heavy objects, they should bend at the knees and lift with their legs rather than their back.
Promote Stress Management
- Help your child develop healthy ways to manage stress, as emotional well-being can impact physical health. This may include activities like mindfulness, relaxation exercises, or engaging in hobbies.

Educate on Body Mechanics
- Teach your child about proper body mechanics for various activities, such as lifting, carrying, and playing sports. This knowledge can help prevent injuries
By incorporating these preventive tips into your child’s routine, you can promote good musculoskeletal health and reduce the risk of back pain. If your child does experience persistent or severe back pain, consult with a spine surgeon for further evaluation and guidance